Pain occurs whenever tissues are being damaged, and it causes the individual to react to remove the pain stimulus.
Hyperalgesia : Increased sensitivity to pain
Types of pain – fast pain and slow pain
| FAST PAIN | SLOW PAIN | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Felt within 1 second after a pair stimulus is applied. | 1. Felt after 1 second or more then increases slowly over many second and sometimes over minutes. | |
| 2. Sharp pain, pricking pain, acute pain and electric pain | 2. Slow burning pain, aching pain, throbbing pain, nauseasis pain and Chronic pain | |
| 3. Not felt in most deep tissues of the body. | 3. Can occur both in the skin and in almost any deep tissue or organ. | |
| 4. Stimulus: mechanical and Thermal | 4. Stimulus : mechanical, thermal and chemical | |
| 5. A-delta fibres | 5. C fibres | |
| 6. Velocity : 6-30 m/s | 6. 0.5-2 m/s | |
| 7. Neospinothalamic tract | 7. Paleospinothalamic tract | |
| 8. Neurotransmitter: Glutamate | 8. Substance P and glutamate |
PAIN RECEPTORS AND THEIR STIMULUS
Pain receptors are free nerve endings and pain stimulus can be :
1- Mechanical
2-Thermal
3- Chemical –
- bradykinin
- serotonin
- histamine
- K+ ions
- acetylcholine
- proteolytic enzymes
- prostaglandins : example – substance P – enhance the sensitivity of pain endings but do not directly excite them.
Non adapting nature of pain receptors : Unlike other receptors of the body, pain receptors adapt very little and sometimes not at all.
Rate of tissue damage as a stimulus for pain
The average person begins to perceive the pain when the skin is heated above 45oC.
The intensity of the pain is closely (co-related) with the rate of tissue damage from –
- heat
- bacterial infections
- tissue ischemia
- tissue contusion
- muscle spasm
DUAL PAIN PATHWAY IN THE CORD AND BRAINSTEM
When entering the spinal cord, the pain signals take two pathways to the brain :
- Neospinothalamic tract
- Paleospinothalamic tract
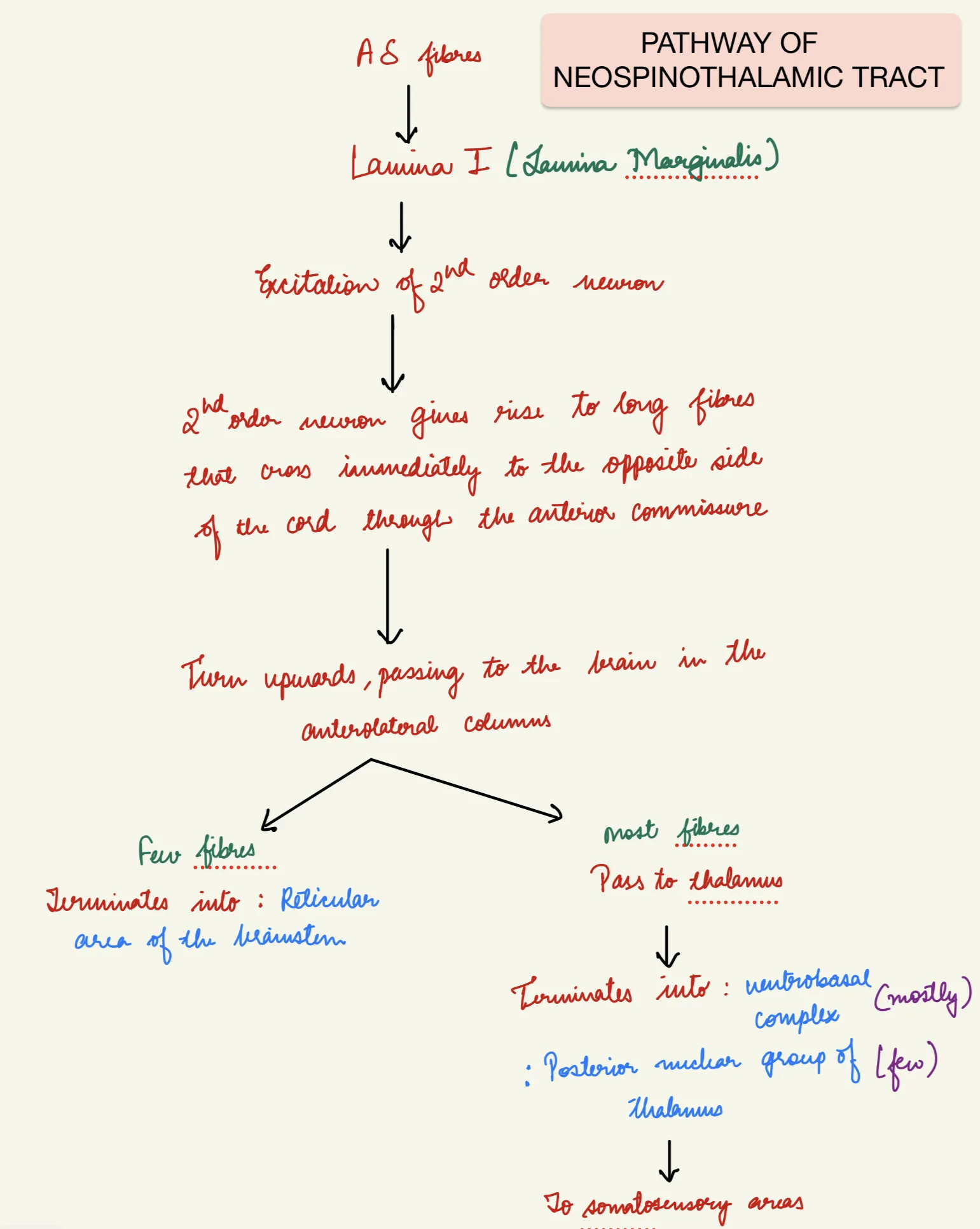
NEOSPINOTHALAMIC TRACT
- For fast pain
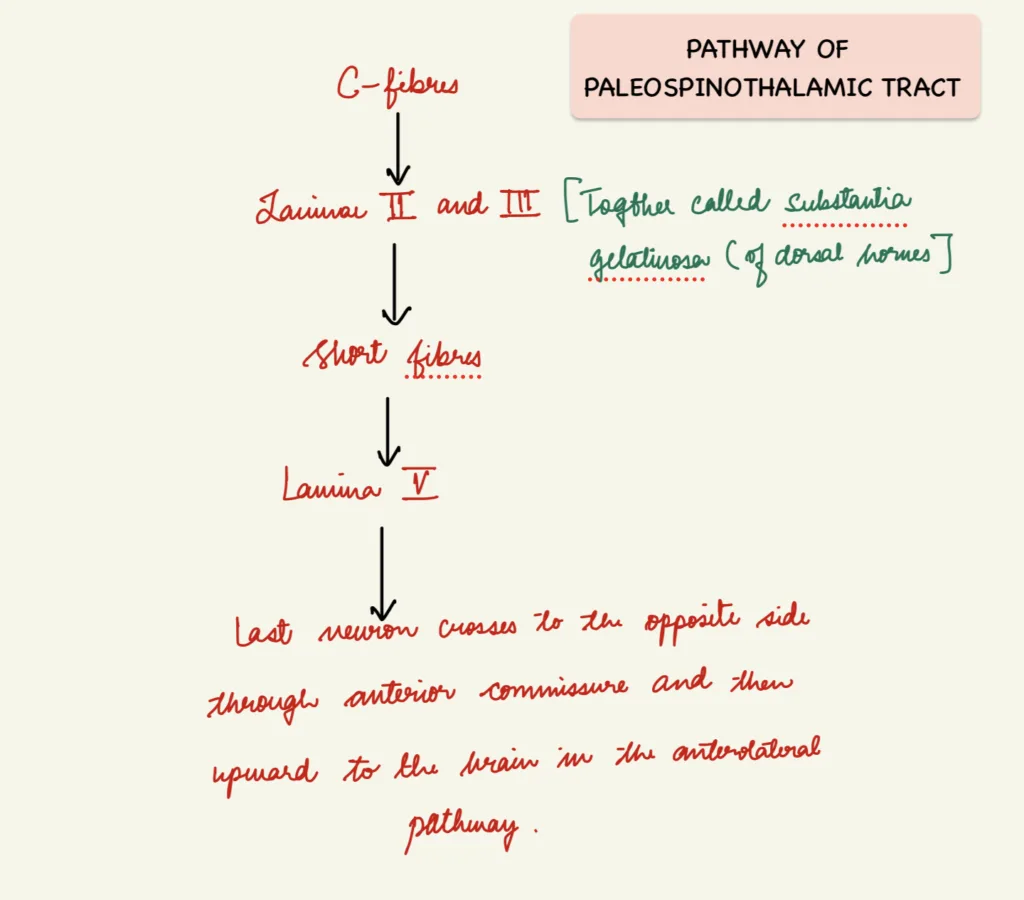
PALEOSPINOTHALAMIC PATHWAY
- for slow chronic pain
- older system
GET CONNECTED TO US ON OUR INSTAGRAM PAGE – https://www.instagram.com/medmaps.in/
FOR PHYSIOLOGY SECTION VISIT – https://medmaps.in/category/notes/physiology/

0 Comments