FEATURES
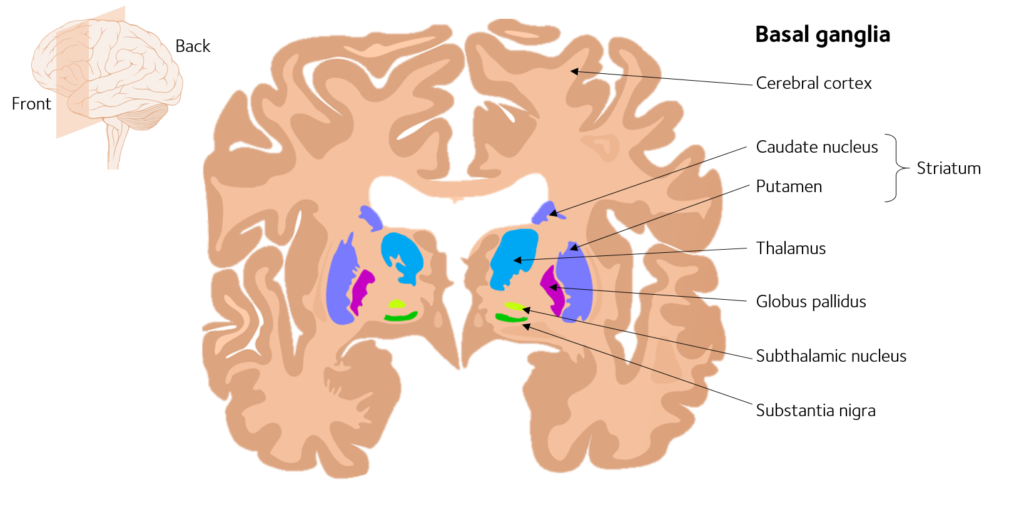
The basal ganglia (nuclei) are subcortical and intracerebral masses of grey matter forming important parts of extrapyramidal system. It includes :
1- Corpus striatum –
- (a) Caudate nucleus
- (b) Lentiform nucleus – (i)Putamen (lateral part) (ii) Globus pallidus (medial part) .
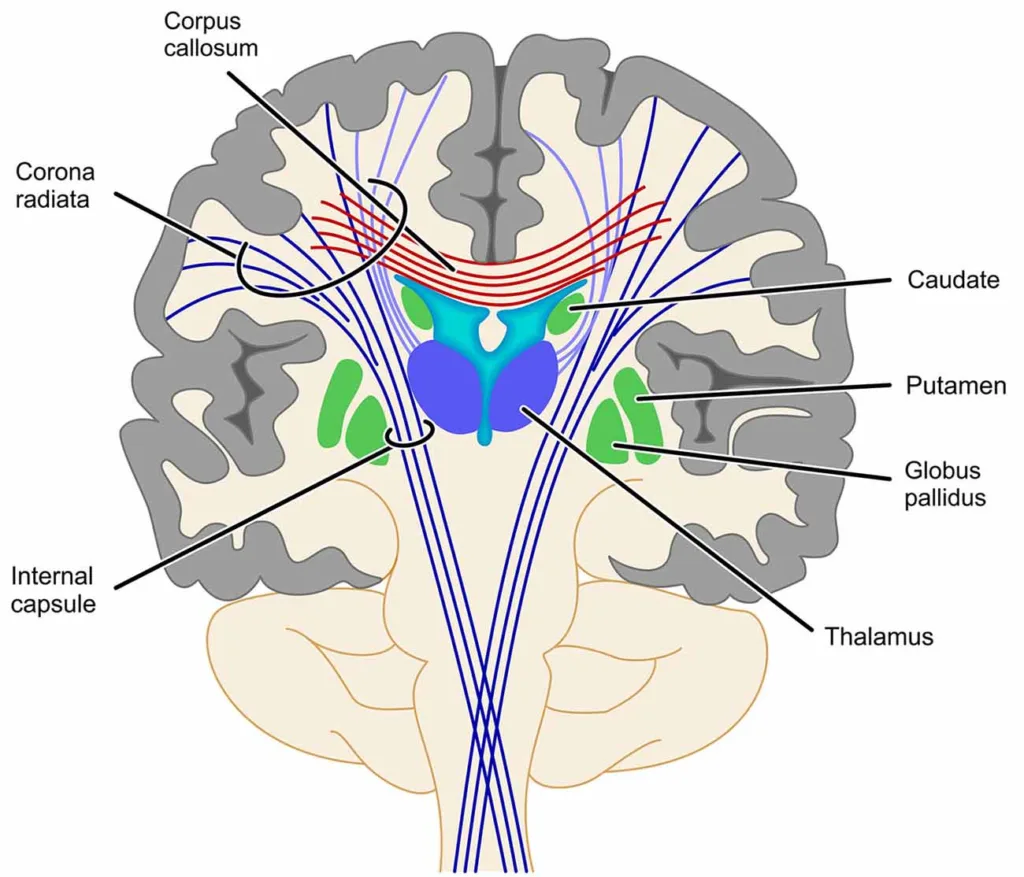
Both nuclei are divided partially by the internal capsule and interconnected by a few bands of grey matter below the anterior limb of the internal capsule.
2- Amygdaloid body
3- Claustrum
CORPUS STRIATUM
Consist of caudate nucleus and lentiform nucleus.
CAUDATE NUCLEUS
- C- shaped or comma shaped nucleus
- Surrounded by the lateral ventricle
- The concavity of ‘ C ‘ encloses the thalamus and the internal capsule
Parts of caudate nucleus
- Head
- Body
- Tail
1. Head : – forms –
(i) Floor -anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
(ii) Medial wall – Anterior limb of the internal capsule
2. Body : – Forms –
(i) Floor – Central part of the lateral ventricle
Location : Medial to the posterior limb of the internal capsule
Stria terminalis and thalamostriate vein separate it from the thalamus
Relation : Superiorly – (i) Fronto – occipital bundle (ii) Corpus callosum
3. Tail : – Forms –
(i) Roof – Inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
Ends by joining the Amygdaloid body at the temporal pole.
Relation
- Medial – Stria terminalis
- Lateral – Tapetum
- Superior – (i) Sublentiform part of the internal capsule
(ii) Globus pallidus
LENTIFORM NUCLEUS
- Large, lens shaped (biconvex) nucleus
- Forms lateral boundary of the internal capsule
- Location – Beneath the insula and the claustrum
3 surfaces
1: Lateral surface : Convex
Related to external capsule – the claustrum, insula, the outermost capsule, and is grooved by the lateral striate arteries.
2: Medial surface – More convex
Related to internal capsule, Caudate nucleus and the thalamus
3: Inferior surface –
Related to sublentiform part of the internal capsule and grooved by anterior commissure fibres.
Parts of lentiform nucleus
Thin lamina of white matter divides the lentiform nucleus into 2 parts :
1. Putamen : –
- Larger lateral part
- Contains small cells
- Structurally similar to Caudate nucleus
2. Globus pallidus : –
- Smaller, medial part
- Contains large cells
MORPHOLOGICAL DIVISION OF CORPUS STRIATUM
1. Paleostriatum – Older, primitive part and is represented by Globus pallidus
2. Neostriatum – More recent in development and is represented by the Caudate nucleus and the putamen of the lentiform nucleus
AMYGDALOID BODY
- •Nuclear mass in the temporal lobe
- Location – Anterosuperior to the inferior horn of lateral ventricle
- Topographically- Continuous with the tail of the Caudate nucleus
- Functionally related to stria terminalis
- Part of limbic system
- Afferent- From the olfactory tract
- Efferent- It gives to the stria terminalis which ends in the anterior commissure, the anterior perforated substances and in hypothalamic nuclei.
- Function : Emotional control
CLAUSTRUM
- Saucer shaped nucleus
- Location- Between the putamen and the insula
- Inferiorly, it is thickest and continuous with the anterior perforated substances.
NEURONAL CIRCUITRY OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
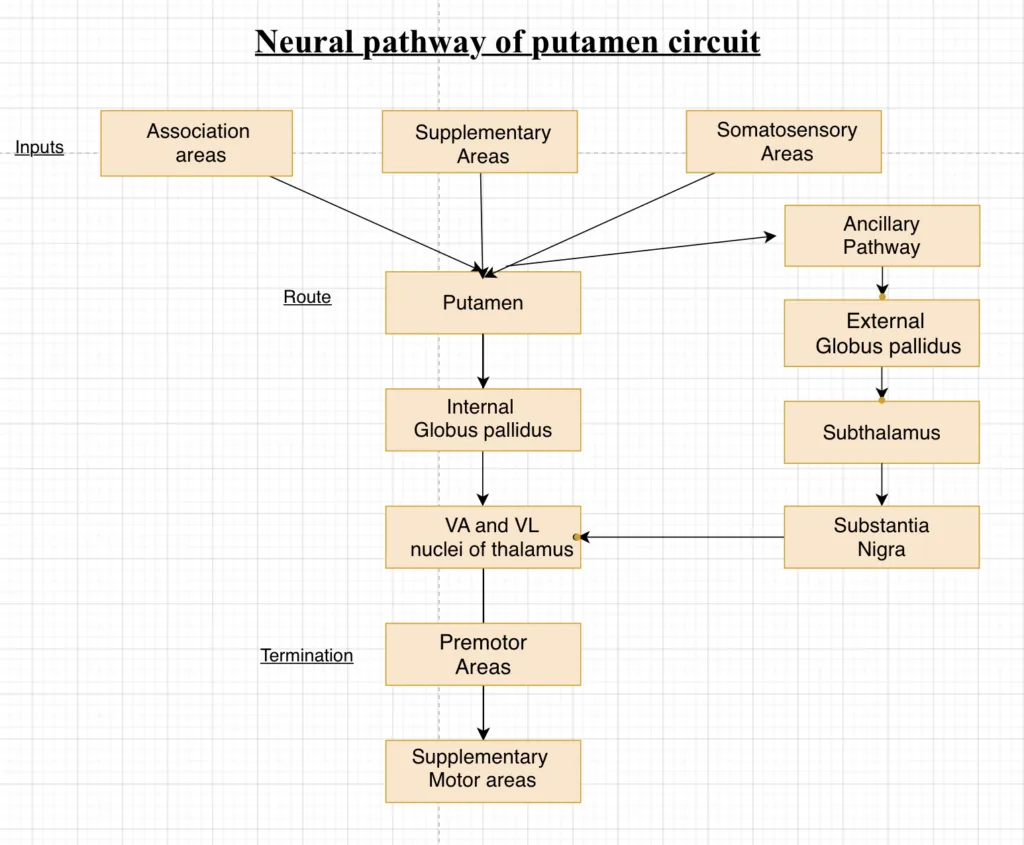
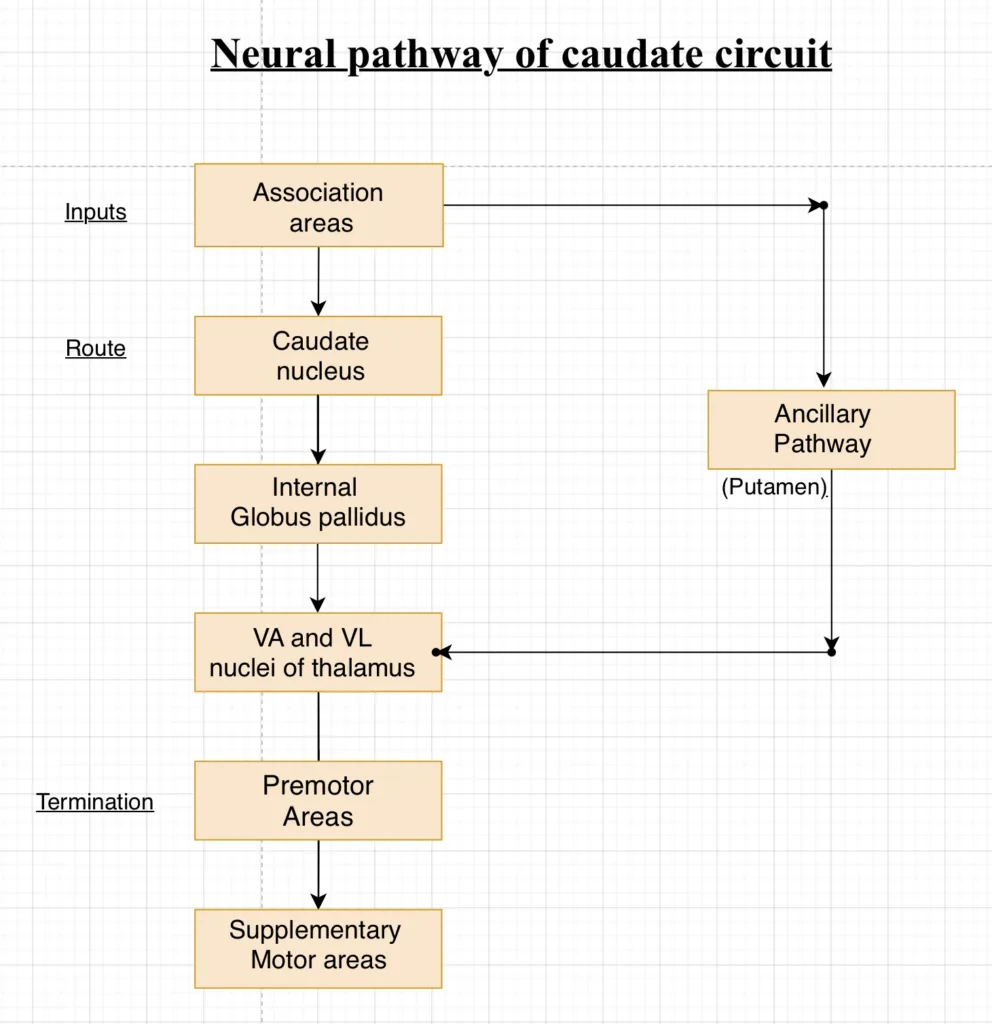
The anatomical connections between the basal ganglia and other part brain elements that provide control are complex. Two major circuits, the Putamen circuit and Caudate circuit.
NEURAL PATHWAYS OF THE PUTAMEN CIRCUIT
NEURAL PATHWAYS OF THE CAUDATE CIRCUIT
DISORDERS
Athetosis : Lesions in the Globus pallidus frequently lead to spontaneous and often continuous writhing movements of a hands, an arm, the neck, or the face.
Hemiballismus : Lesion in the subthalamus often leads to sudden flailing movements of the entire limb.
Chorea : Multiple small lesions in the putamen lead to flicking movements of the hands, face, and other parts of the body.
Parkinson’s disease : Lesions of the substantia nigra lead to the common and extremely severe disease of rigidity, akinesia, and tremors.
FOR ANATOMY SECTION VISIT – https://medmaps.in/category/notes/anatomy/
GET CONNECTED TO US ON OUR INSTAGRAM PAGE – https://www.instagram.com/medmaps.in/
0 Comments