Anal canal is the last part of the Anal canal. It begins at the anorectal junction and ends at the anus.
The anorectal junction is marked by the forward convexity of the perineal flexure of the rectum. The perineal flexure of the rectum is the backward bend at the anorectal junction.
It is longer in males than in females. It facilitates the movement for faecal excretion.
Situation – It is situated below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It lies in the anal triangle of perineum in between the right and left ischioanal fossae.
Length – It is 3.8 cm long.
Extent – It extends from the anorectal junction to the anus.
Direction – It is directed downwards and backwards.
RELATIONS OF THE ANAL CANAL
Anteriorly
- Perineal body is present in both sexes.
- Membranous urethra and bulb of penis is present in males
- The lower end of the vagina is present in females.
Posteriorly
- Anococcygeal ligament
- Tip of the coccyx
Laterally
- Ischioanal fossa
All-round
- Surrounded by the sphincter muscles (helps in keeping the canal closed)
INTERIOR OF THE ANAL CANAL
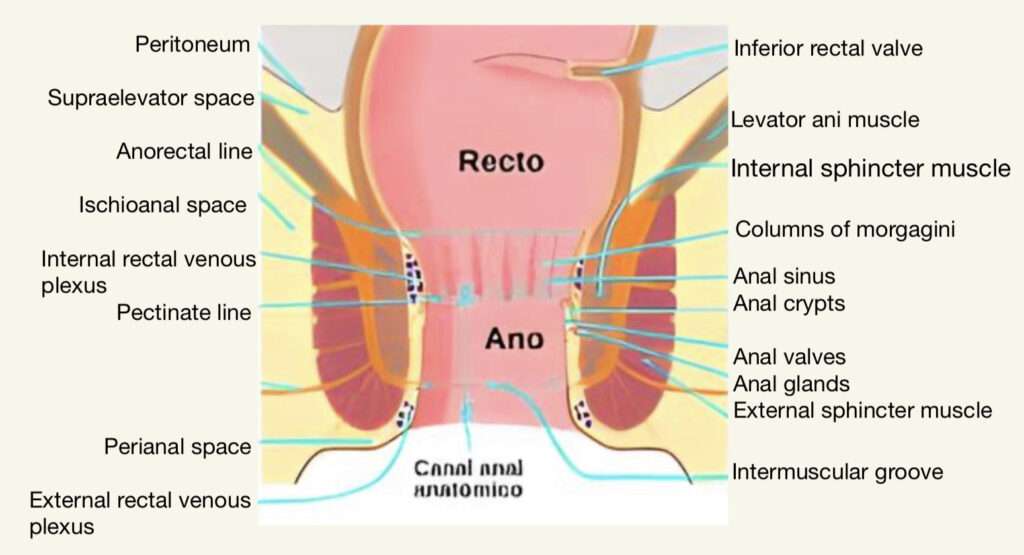
It is divided into 3 parts :-
1- Upper Mucous Part
It is 15 mm long and is lined by a mucous membrane which has 6-10 vertical folds called the anal columns of Morgagni.
These columns are joined together from the lower end by short transverse folds of mucous membrane anal valves.
Each valve has a depression above it, which is called anal sinus.
Anal sinus contains anal glands.
2- Middle Part or Transitional zone
It is also called pecten.
This region starts below the pectinate line and continues till the white line of Hilton which has a whitish appearance and forms its lower limit.
Hilton’s line is situated at the level of the interval between the subcutaneous part of external anal sphincter and the lower border of internal anal sphincter.
It is also 15 mm long.
The mucous over this region has a bluish appearance because of the dense venous plexus that lies between it and the muscle coat.
3- Lower Cutaneous Part
It is 8 mm long.
It is lined by true skin containing sebaceous glands.
MUSCULATURE OF THE ANAL CANAL
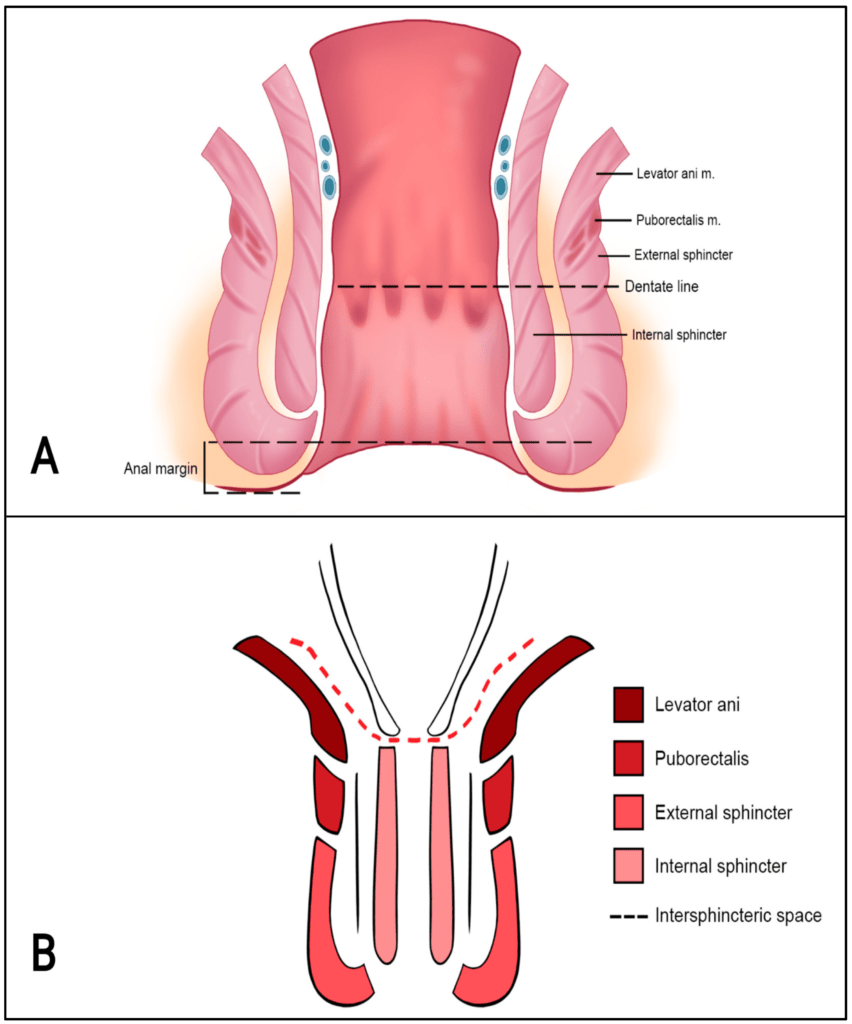
ANAL SPHINCTERS
Internal anal sphincter
- Involuntary in nature
- Formed by thickened circular muscle coat
- Surrounds upper 3/4 of the anal canal (around 30 mm – from upper end of anal canal to white line of Hilton)
External anal sphincter
- Forms a single functional and anatomic entity.
- Voluntary in nature
- Formed by striated muscle
- Nerve supply – Inferior rectal nerve and perineal branch of the fourth sacral nerve .
- Surrounds the whole length of the anal canal and has three parts – subcutaneous, superficial and deep.
- Upper fibres – blend with puborectalis. Anteriorly –
CONJOINT LONGITUDINAL COAT
Formation : Fusion of the puborectalis with the longitudinal muscle coat of the external rectum at the anorectal junction.
Location : Lies between the external and internal sphincters.
When traced downwards, it becomes fibroelastic and at the level of the white line, it breaks up into a number of fibroelastic septa which spread out fan- wise, pierce the subcutaneous part of the external sphincter, and are attached to the skin around the anus called as corrugator cutis ani.
The most lateral of these septa forms the perianal fascia.
The most medial septum forms, the anal intermuscular septum, which is attached to the white line.
ANORECTAL RING
It’s a muscular ring.
Location : Anorectal junction.
Formation : Fusion of the puborectalis, uppermost fibres of the external sphincter and the internal sphincter.
It is easily felt by a finger in the anal canal.
ARTERIAL SUPPLY
1- Above the pectinate line : Superior rectal artery.
2- Below the pectinate line : Inferior rectal artery.
VENOUS DRAINAGE
1- Internal rectal venous plexus or haemorrhoidal plexus : Lies in the submucosa of the anal canal.
Main drainage – Superior rectal vein, but communicates freely with the external rectal venous plexus and so with the middle and inferior rectal veins.
• Important site for portocaval anastomosis.
2- External rectal venous plexus : Lies outside the muscular coat of the rectum and anal canal.
• Lower part is drained by the Inferior rectal veins into internal pudendal vein.
• Middle part by middle rectal vein into internal iliac vein.
• Upper part by superior rectal veins which continues as the inferior mesenteric vein.
3- Anal veins : Arranged radially around the anal margin.
Communicates with the internal rectal plexus and with the inferior rectal veins.
• External piles : Excessive straining during the defecation may rupture one of these anal veins, forming a subcutaneous perianal haematoma known as external piles.
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
1- Above the pectinate line – Internal iliac nodes ( with those of the rectum )
2- Below the pectinate line – Medial group of the superficial inguinal nodes.
NERVE SUPPLY
1- Above the pectinate line – Automatic nerves both sympathetic ( inferior hypogastric plexus – L1, 2) and parasympathetic ( pelvic splanchnic – S2, 3, 4).
Pain sensations are carried by both of them.
2- Below the pectinate line – Somatic nerves ( inferior rectal – S2, 3, 4 ).
3- Sphincters • Internal sphincter – Contraction by sympathetic and relaxation by parasympathetic nerve.
• External sphincter – Supplied by the inferior rectal nerve and perineal branch of the 4th sacral nerve.
CLINICAL ASPECT
1- Internal piles or true piles – Dilation of the internal rectal venous plexus.
They occur above the pectinate line, therefore painless.
Primary piles – occurs at 3,7 and 11 o’clock position of the anal wall (view – lithotomy position)
Secondary piles – if it occurs other than the above mentioned positions, it is known as secondary piles.
2- External piles – They occur below the pectinate line therefore very painful.
3- Fissure in ano – Anal fissure is caused by rupture of one of the anal valves generally due to constipation
4- Fistula (abnormal, epithelialised track connecting two cavities) in ano – Caused by spontaneous rupture of the abscess around the anus.
FOR ANATOMY SECTION VISIT – https://medmaps.in/category/notes/anatomy/
GET CONNECTED TO US ON OUR INSTAGRAM PAGE – https://www.instagram.com/medmaps.in/

0 Comments